Micron Technology: a Hidden Gem in the Semiconductor Industry? - 25/12/2022
Gaining Insights into Micron's Future Outlook through Fundamental, Quantitative, and Technical Analysis.
Welcome, fellow seekers!
In today’s article, we will dig deep into Micron Technology, Inc. (NASDAQ:MU) which is a leading global provider of advanced semiconductor solutions. With a market capitalization of over $100 billion, Micron is a significant player in the semiconductors industry. Here, we will provide a comprehensive analysis of Micron's stock, including a review of the company's financial performance, competitive landscape, and future growth prospects. Whether you are a current shareholder or considering adding Micron to your portfolio, this article will provide valuable insights into the company's potential as an investment.
Who are Micron Technology and what do they do?
Micron Technology is a leading provider of memory and storage products worldwide. The company operates through four segments: Compute and Networking, Mobile, Embedded, and Storage. It offers a range of memory and storage technologies, including DRAM, NAND, and NOR products, for various markets such as cloud servers, enterprise, client, graphics, networking, industrial, and automotive. In addition, the company provides SSDs and component-level solutions for the enterprise and cloud, client, and consumer storage markets, as well as discrete storage products in component and wafers for the automotive, industrial, and consumer markets. Micron Technology sells its products through a variety of channels, including direct sales, independent sales representatives, distributors, retailers, and online sales. The company was founded in 1978 and is headquartered in Boise, Idaho.
At the time of writing this article, the price of MU 0.00%↑ is exactly 50.20$.
1. Industry Analysis
The semiconductor industry is a vital and rapidly growing sector that plays a key role in the global economy. Semiconductor products, which include microchips, memory devices, and other electronic components, are essential components of many electronic devices and systems, including computers, smartphones, and automobiles. The demand for these products has been growing rapidly in recent years, driven by the increasing use of electronic devices and the emergence of new technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and 5G connectivity.
According to a recent report by Fortune Business Insights, the global semiconductor market is expected to grow from $573.44 billion in 2022 to $1,380.79 billion by 2029, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.2%. This growth is being driven by a number of factors, including the increasing adoption of electronic devices, the growth of the IoT, and the expansion of 5G networks. In addition, the rise of AI and machine learning has increased demand for high-performance semiconductor products, particularly in the data center and cloud computing sectors.
The semiconductor industry is highly competitive, with a large number of players operating at different points in the supply chain. Many of the world's leading semiconductor companies are based in the United States, including Intel, Qualcomm, and TSMC. However, the industry is also dominated by a few large players, such as Samsung, SK Hynix, and TSMC, which have significant market share and manufacturing capabilities. These companies have invested heavily in research and development (R&D) in order to remain at the forefront of the industry, and have developed leading-edge technologies such as 3D NAND and 7nm processes.
One of the key challenges facing the semiconductor industry is the increasing complexity of chip design and production. As chips have become more sophisticated and feature-rich, the cost of developing and producing them has increased significantly. This has led to a rise in the cost of semiconductor products, which has put pressure on device manufacturers and consumers. In addition, the industry is facing a shortage of skilled workers, particularly in the design and R&D areas. This shortage is expected to worsen in the coming years, as the number of STEM graduates in the United States falls and the number of experienced designers leaving the industry increases.
Another challenge facing the industry is the increasing competition from other regions, particularly China. Chinese companies have been investing heavily in semiconductor R&D and manufacturing in recent years, and have made significant strides in catching up with their international counterparts. This has led to concerns about the competitiveness of the US semiconductor industry, and there are concerns that the United States could lose its leadership position in the sector if it does not take action to address these challenges.
1.1 Industry Metric
For our industry analysis we will use the VanEck Semiconductor ETF. The SMH 0.00%↑ ETF tracks the performance of the 25 largest US-listed semiconductor companies and offers concentrated exposure to the US semiconductor industry. It is equally split between giant, large, and mid cap size companies and has a shallow portfolio with the top ten holdings accounting for over two-thirds of assets.
First let’s see how the ETF performed over the past year compared to the market.
Based on the data, it appears that the semiconductor industry has underperformed the overall market over the past year. The SMH ETF has experienced a return of -27.95% over the past year, while the SPY 0.00%↑ ETF has experienced a return of -15.00%. This indicates that the semiconductor industry has been more affected by negative market conditions compared to the overall market. The SMH ETF has also had higher annual volatility compared to the SPY ETF, with a volatility of 42.29% compared to 24.12%. This suggests that the semiconductor industry has been more susceptible to price fluctuations compared to the overall market. In the shorter term, the SMH ETF has also underperformed the SPY ETF, with returns of -7.76% and -4.90% over the past week and -4.33% and -3.47% over the month, respectively. Overall, the data suggests that the semiconductor industry has been impacted by negative market conditions, but has shown some signs of resilience over the past six months.
As of December 21, the last day price for Micron Technology (MU) was $50.68, indicating a downward trend compared to its 50 and 200 day moving averages of $55.55 and $61.91, respectively. Meanwhile, the Semiconductor ETF (SMH) was priced at $207.66, exhibiting relatively stable performance over the past 50 days but a downward trend compared to its 200 day moving average of $219.94. The S&P 500 Index (SPY) was priced at $380.54, reflecting a negative trend compared to its 50 and 200 day moving averages of $384.79 and $397.78, respectively. These trends suggest that all three stocks have experienced a decline in recent months.
1.2 Industry Breadth Analysis
According to the 50-Day Weighted Moving Average Breadth of 28% for the Semiconductor industry, there seems to be a lower level of participation within the sector currently. This could be due to a lack of excitement or investment interest in the industry, or it could simply reflect a concentration on a smaller group of companies within the sector. Additionally, the significant decline in the past month suggests that a majority of stocks within the industry have had a challenging month and have fallen below their 50-day moving average.
The 200-Day Weighted Moving Average Breadth has seen a drop to 40%. This suggests that there may be a lack of broad participation in the sector, with potentially only a few companies driving the industry's performance. This could be a sign of investor caution or disinterest in the sector, or it could reflect a more narrow focus on a smaller number of companies within the industry. The sharp drop in the 200-Day Breadth over the past month also indicates that the long-term trend for the industry has shifted towards bearish.
2. Fundamental Analysis
2.1 Revenue
Let’s first check at the company’s revenue structure to gain more insight as of where the money are coming in and what’s the latest reported numbers. The below graph is taken from their FQ1 2023 Financial Results report to its investors.
As we can see the highest share of the revenue goes to Compute and Networking (CNBU). It generates revenue from memory products and solutions sold to the client, cloud server, enterprise, graphics, and networking markets. The segment saw -49% Y/Y Change and had a -40% quarter-to-quarter performance.
The Embedded and Storage units saw a -18% and -41% drop Y/Y change. The worst performer was the Mobile Busniess Unit which saw a 66% drop from the previous year, which isn’t a surprise as the end consumer demand has seen a huge drop.
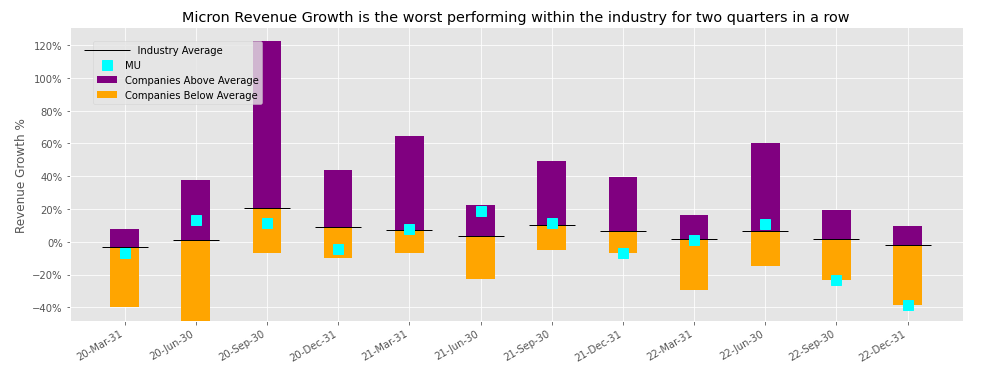
Compared to the Industry, Micron has the worst revenue growth and is sitting at the bottom of the pack for 2 consecutive quarters.
2.2 Net Profit Margin
Overall the company's Net Profit Margin has been historically around the industry average, however in the most recent quarter, it was at the bottom of the pack. That can suggest that the efficiency of the company has decreased significantly, however, we can see that the profit margin has shrunk for the whole industry as well.
2.3 Costs
2.3.1 Cost of Revenue
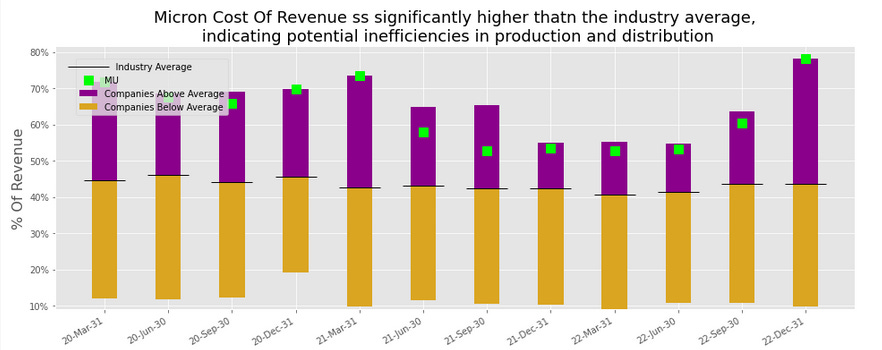
The cost of revenue of Micron is significantly higher than the industry average which can indicate that there are inefficiencies in the production and distribution costs.
We can now take a look at how the cost of revenue was trending over time within the company. We can see that it is steadily increasing over the past year, suggesting that the company may be facing higher costs for raw materials or labor, or that it is expanding its product line and incurring additional costs as a result.
2.3.2 Research and Development Expenses
Research and Development expenses have risen sharply in the last quarter. We can treat this as a positive sign for the company’s future growth, as it suggests that it is actively working on developing new offerings that will possibly generate revenue in the future. But it is important to consider the context in which the R&D expenses are occurring. If the company is not generating enough revenue, an increase in expenses can put additional strain on its financial resource
2.3.3 Interest Expenses
The interest expenses have risen sharply in the last quarter indicating that the cost of debt has risen or that the company is relying on more borrowing to finance its operations. Given the FED policy of rising interest rates, the higher interest expenses can be detrimental to profitability and the costs of doing business
2.4 Debt
The Debt Growth in the last quarter was relatively small. Historically the company maintained a level below or around the industry average indicating that Micron has stable and good debt management relative to its competitors
The company has a debt-to-equity ratio of 0.20, which means it has a relatively low amount of debt compared to its equity. This is a good sign of financial stability and responsible financial management, as the company is not relying heavily on borrowing to finance its operations and growth. A low debt-to-equity ratio may also indicate that the company has a strong balance sheet and is able to generate enough profits to support its operations and pay off its debts.
2.5 Inventory
Micron's inventory is valued at the lower of its cost or the amount it can reasonably be sold for, and the cost is determined using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method. This means that the company assumes that the first items placed in inventory are the first ones sold. In order to determine the net realizable value, Micron makes projections about future selling prices and volumes. However, the volatile nature of the semiconductor market can impact these estimates. To account for this, Micron groups all of its inventories (including DRAM, NAND, and other memory) together when performing the lower of cost or net realizable value analysis. As of September 1, 2022, a 5% change in the estimated selling prices would have resulted in a $337 million change in the estimated net realizable value of the company's inventory.
*The information is taken directly from the company K-10 Form
The inventory levels have seen a rapid growth in the last quarter which can indicate us a decrease in the overall sales or overstocking. The high inventory levels can lead to higher cost of goods sold, which can lead to lower gross profit margin.
The effect can be clearly seen in the below graph. We can see that the Gross Profit Growth has fallen and is currently in the negative territory. This could mean that the company is not effectively managing its costs, pricing its products appropriately, or generating sufficient sales. A decline in gross profit growth can also be a sign of increased competition or changing market conditions
.
2.6 Dividends
Micron only started paying dividends in the middle of the previous year. The company's dividend yield for the current fiscal year is 0.75%, and its payout ratio is 5.55%. The dividend per share has increased significantly from 0.10 to 0.43 over the past year.
2.7 Valuation Models
Based on our fair value models, the average price of Micron stock is estimated to be $199 per share. However, the price-to-earnings model suggests a fair price of $252 and the free cash flow model indicates a share price of $296. The only model that gives a valuation close to the current share price is the sales model. It's worth noting that these numbers should be taken with a grain of salt, but the general consensus is that the current price is undervalued.
3. Quantitative Analysis
3.1 Earnings beats
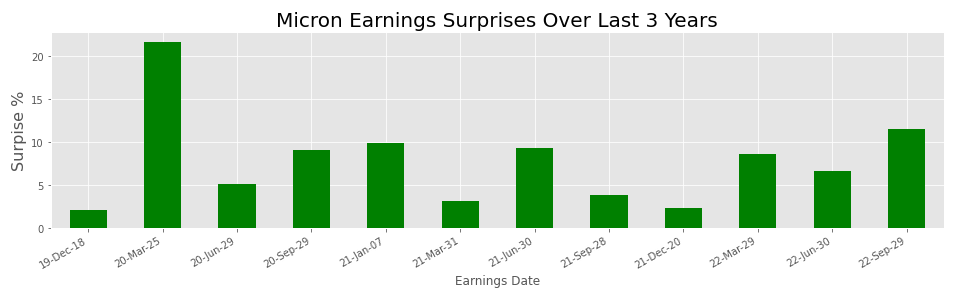
In the course of time Micron Technologies has consistently beaten earnings estimates. The average surprise percent is 7.8, which demonstrates the company’s track record of consistently beating the analysts’ estimates.
3.2 Analysts Ratings
The below graph illustrates the rating system used. A rating of 1 represents a "Sell," "Negative," or "Underperform" recommendation, while a rating of 5 indicates a "Strong Buy," "Outperform," or "Market Outperform" recommendation. We can see that the overall sentiment is a “Buy” while some of the grading companies are giving it a “Strong Buy”. Only Morgan Stanley and Piper Sandler are currently rating it “Underweight”.
3.3 Dollar Flow
Our proprietary dollar flow model doesn’t show any significant inflow or outflow recently. The last time there was any significant movement was on November 30th and since then the stock has seen a 7$ decline in price.
3.4 Insider Transactions
There have been no insider transactions recently.
3.5 Quant Filter
The stock appears to be oversold based on our Quant Filter, which is currently below its lower band. This could indicate a potential turning point and a reversal to the upside.
3.6 Institutional Investors
Vanguard Group has consistently acquired shares of Micron Technologies throughout the year. The company is currently the biggest owner, holding 8.19% of the total shares of the company. This demonstrates confidence in Micron's potential and can be seen as a positive indicator for investors.
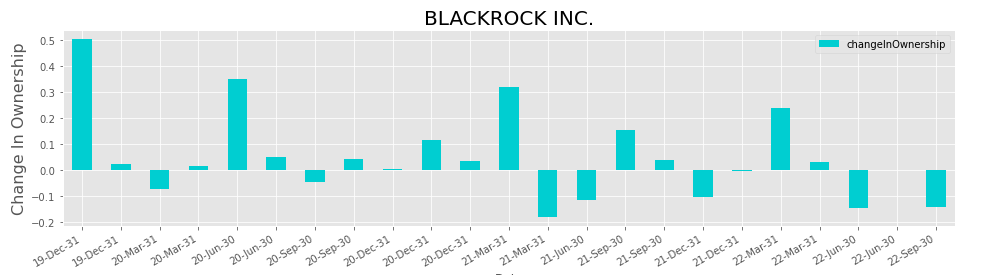
BlackRock's ownership of Micron Technologies has had its ups and downs over time, but in the last reported quarter, the asset manager reduced its ownership percentage by 1.87%. This resulted in a decrease of 5.62% in the weight of Micron Technologies in BlackRock's portfolio. Despite this, BlackRock is still the second largest owner of Micron Technologies, holding 7.42% of the company's shares.
Capital Research Global Investors has been steadily increasing its ownership of Micron Technologies for the last two years. In the latest quarter, the fund saw a significant increase in its holdings of the company, with a 19.5% growth in the weight of Micron Technologies in its portfolio. As a result, Capital Research Global Investors is now the third largest owner of Micron Technologies.
4. Price Action and Technical Analysis
Micron Technologies has been on a downward trend over the last year, as shown in the chart. The stock is currently approaching a 3-year-long support level, where we can see a double-bottom pattern forming. This upcoming period will be key in determining the direction the stock takes. Technical analysis suggests that the price may bounce off the support level and continue to move upward.
Our analysis of the daily chart supports our belief that Micron Technologies' stock is likely to see a reversal and test the previous high as it searches for a resistance level. The formation of a double-bottom pattern further confirms this potential uptrend in the near future.
Conclusion
Micron Technologies, a leading semiconductor company, has been facing challenges in its revenue growth recently, especially in its Mobile Business Unit, which saw a 66% drop in the previous year. The company's net profit margin has also been below the industry average, indicating a decline in efficiency. Micron has higher than average production and distribution costs, which could be an indication of inefficiencies in these areas. However, the company has increased its research and development expenses, which could potentially lead to future growth. It's important to consider the context of these expenses, however, as they may strain the company's financial resources if it is not generating enough revenue. Interest expenses have also risen, which may be due to rising interest rates and could negatively impact profitability. While Micron has a relatively low debt-to-equity ratio, indicating financial stability and good financial management, its increasing inventory could potentially lead to lower profits or write-downs in the future.
And what do you think about Micron Technologies, please do share your thoughts in the comment section below. I would love to hear your analysis.
Also if you have any particular stock in mind and you want to see a comprehensive analysis of it, do not hesitate to suggest it!
Disclaimer: Please note that the information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, legal, or professional advice. The information provided should not be relied upon as a substitute for financial, legal, or professional advice. Before making any decision, it is important to consider all relevant information and consult with a professional who can provide personalized advice based on your specific circumstances. The author and publisher of this article cannot be held liable for any actions taken based on the information provided. This is not a recommendation to buy or sell any specific securities or financial instruments.